Dr. Ellen C. Breen

Ellen C. Breen, PhD. My early training was in molecular/cell biology at the University of Vermont, where I received a PhD in Biochemistry under the supervision of Dr. Kenneth Cutroneo. This research focused on identifying the subpopulations of fibroblast, initiating a pulmonary fibrotic response. I continued to investigate the regulation of extracellular matrix proteins in the laboratory of Dr Gary Stein at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center where I study the role of Vitamin D in the in vivo transcriptional regulation of osteocalcin, a key gene involved in osteoblast differentiation. Upon joining the Division of Physiology at UCSD in 1994, I continued to study the extracellular matrix protein in the lung and their dynamic response to mechanical strain. I also expanded my research focus to investigate the peripheral oxygen transport system and developed several in vivo mouse models to understand how O2 is made available to skeletal muscle mitochondria in response to exercise training and chronic pulmonary disease.
Currently, the lab has two major projects:
- It aims to understand the inflammatory and O2 regulatory response to SARS-CoV-2 and how this may be attenuated by IL-33 and IL-1ß protein modulators.
- To understand the role of N-glycans in peripheral O2 transport. These mechanisms are hypothesized to allow terrestrial mammals to endurance exercise and marine mammals to dive for extended periods of time.
Laboratory Members
Donivian Al-Dikka

Donivian is currently working on his Masters Thesis project through the Department of Biology. His is investigating how mice with an inactivated CMAH gene utilized O2 and metabolites more efficiently to improve skeletal muscle fatigue resistance. This research has included PCr clamp measurements of mitochondrial respiration using a high-resolution respirometer and mapping the biochemical pathways using 13C acetate and pyruvate in resting and contracting skeletal muscle from Cmah null mice.
Brad Parks

Brad is also working on experiments to complete a Masters thesis through the Department of Biology. He is investigating the exercise-induced neurogenic response in mice that have extended sialic acid chains due to the over expression the ST8Sia2 gene.
Nathaniel Lightle

Nathaniel is an undergraduate member of the lab. He is studying a mouse model in which Cmah expression is regulated specifically in skeletal muscle of adult mice. His goal is to evaluate the exercise acute and training responses and elucidate the skeletal muscle and vascular changes in O2 delivery and utilization that may control a change in exercise endurance.
Rita Aziz

Rita is an undergraduate member of the lab. Her research focuses on understanding how O2 in regulated in the peripheral system of diving marine mammals. She is working on developing methods to map the three-dimensional spatial organization of skeletal muscle mitochondria from pinnipeds and cetaceans. She is also performing experiments to measure O2 content as it relates to lipid composition and ordering in plasma membranes.
Audrey Chong

Audrey is an undergraduate member of the laboratory. She is working on a COVID-19 project and is studying mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunits. Audrey is characterizing changes in O2 utilization by measuring lung function and the breathing controlled by neural centers, the carotid body and nucleus tractus solitaries (NTS).
Hieu Vu

Hieu is also an undergraduate member of the laboratory working on the COVID 19 project. He has been evaluating the pulmonary inflammatory cell response in mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins. More recently he has begun to evaluate breathing control through analysis of breathing patterns collected by diaphragm electromyography (EMG).
Anagha Pashilkar

Anagha is an undergraduate member of the laboratory. She is working with a lung organoid model that we challenge with cigarette smoke extract and SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunits. Using this model, she is measuring the activation of IL-33 and disruption of the alveolar capillary barrier (increased apoptosis and proliferation). Using this human organoid model she will test modulators of IL-33 that she prepares in Dr. Jennings’ laboratory in the Department of Biochemistry and Chemistry at UCSD.
Christine Nguyen

Christine is an undergraduate member of the laboratory. Her current project focuses on modeling the three-dimensional organization of the skeletal myofiber mitochondrial network in mice with and without the Cmah gene.
Research
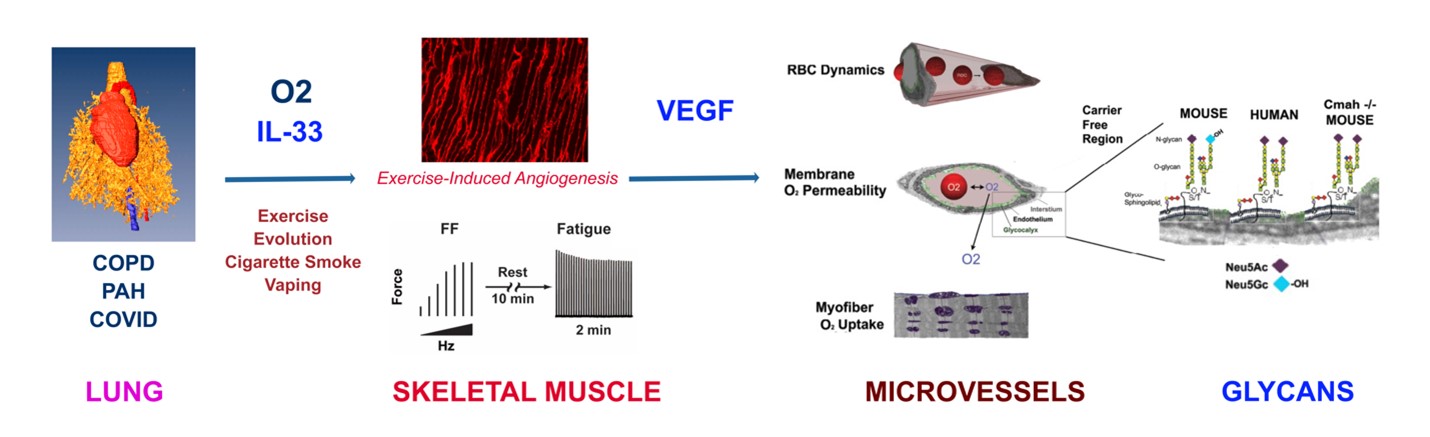
Our laboratory takes an integrative physiology approach to investigate how oxygen (O2) is made available and utilized by tissues and cells throughout the body. We investigate the interactions between the pulmonary system, skeletal muscle and even how this effects the brain. In the lung, we have looked at several conditions that can impair lung function and oxygen delivery, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease caused by cigarette smoke, pulmonary hypertension, and most recently, COVID-19. One of our main focuses is to look at the effects of exercise to increase both the number of capillaries supplying skeletal myofibers and the regulation of O2 delivered by the flow of red blood cells through micro-vessels. Interestingly, humans are unique in that they have the ability to endurance exercise, a characteristic that evolved about 2 million years ago, around this same time period in which humans inactivated a gene called CMAH. This encodes a hydroxylase which adds a -OH on the end of sialic acid chains that coat cell membranes. Deletion of CMAH in mice, giving them a more human-like endothelial surface layer, results in greater exercise endurance. Thus, we are investigating how this genetic change, which occurred at a key time in the evolution of both humans and diving mammals, plays a key role in the final steps of the oxygen transport system. This is the step in which oxygen is transferred from hemoglobin in red blood cells, across several cell layers coated with glycoproteins to reach mitochondria with in skeletal myofibers.
Publications
Original Research Articles
- Breen, E., V.M. Falco, M. Absher and K.R. Cutroneo. 1990 Subpopulations of Rat Lung Fibroblasts with Different Amounts of Type I and Type III Collagen mRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 265:6286-6290.
- Scheme’s, G., E. Breen, T.A. Owen, M.A. Aronow, G.S. Stein, and J.B. Lian. 1991. Influence of Dexamethasone on the Vitamin D-Mediated Regulation of Osteocalcin Gene Expression. Cellular Biochem. 47:184-196.
- Breen, E., S. Schull, S. Burne, M. Absher, J. Kelley, S. Phan, and K.R. Cutroneo. Bleomycin Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor-beta mRNA in Rat Lung Fibroblasts. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 6:146-152.
- Bortell, R., T.A. Owen, J.P. Bidwell, P. Gavazzo, E. Breen, A.J. van Wijnen, H.F. DeLuca, J.L. Stein, JB Lian and G.S. Stein. 1992. Vitamin D-Responsive Protein-DNA Interactions At Multiple Promoter Regulatory Elements that Contribute to the Level of Rat Osteocalcin Gene Expression. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89:6119-6123.
- Breen, E., R. Ignotz, J.L. Stein, G.S. Stein, and J.B. Lian. TGF-ß Alters Growth and Differentiation Related Article Gene Expression in Proliferating Osteoblasts In Vitro Preventing Development of the Mature Bone Phenotype. J. Cellular Physiology. 160:323-335.
- Breen, E.C., A.J. van Wijnen, J.B. Lian, G.S. Stein, J.L. Stein. In Vivo Occupancy of the Vitamin D Responsive Element in the Osteocalcin Gene Supports Vitamin D Dependent Transcriptional Upregulation in Intact Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91:12902-12906.
- Breen, E.C., E.C. Johnson, H. Wagner, H.-M. Tseng, L.A. Sung and P.D. Wagner. Angiogenic Growth Factor mRNA Responses in Muscle to a Single Bout of Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 81:355-361.
- Berg, J.T., Z. Fu, E.C. Breen, H.-C. Tran, O. Mathieu-Costello and J.B. West. High Lung Inflation Increases mRNA Levels of ECM Components and Growth Factors in Lung Parenchyma. J. of Appl. Physiol. 83:120-128.
- Parker, J.C., E.C. Breen and J.B. West. High Vascular and Airway Pressures Increase Interstitial Protein mRNA Expression in Isolated Rat Lungs. J. Appl. Physiol. 83:1697-1705.
- Shalhoub, V., F. Aslam, E. Breen, A. Wijnen, R. Bortell, G.S. Stein, J.L. Stein and J.B. Lian. Multiple Levels of Steroid Hormone-Dependent Control of Osteocalcin During Osteoblasts Differentiation: Glucocorticoid Regulation of Basal and Vitamin D Stimulated Gene Expression. J. Cellular Biochem. 69:154-168.
- Roca, J., T. Gavin, M. Jordan, N. Siafakas, H. Wagner, H. Benoit, E. Breen, P. Wagner. 1998. Angiogenic Growth Factor mRNA Responses to Passive and Contraction-Induced Hyperperfusion in Dog Skeletal Muscle. Appl. Physiol. 85:1142-1149.
- Berg, J.T., E.C. Breen, Z. Fu, O. Mathieu-Costello and J.B. West. Alveolar Hypoxia Causes Increased Gene Expression of Extracellular Matrix Proteins and PDGF-B in Lung Parenchyma. Amer. J. of Resp. and Critical Care Med. 158(6):1920-8.
- Breen, E.C., Z. Fu, H. Normand. 1999. Calcyclin mRNA is Increased by Mechanical Strain in Fibroblasts and Lung. Amer. J. of Respir. Cell & Mol. Biol. 21:746-752.
- Breen, E.C. Mechanical Strain Increases Type I Collagen Expression in Pulmonary Fibroblasts In Vitro. J. of Appl. Physiol. 88:203-209.
- Gavin, T.P., D.A. Spector, H. Wagner, E.C. Breen, P.D. Wagner. Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition Attenuates the Skeletal Muscle VEGF mRNA Response to Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 88:1192-1198.
- Gavin, T.P., D.A. Spector, H. Wagner, E.C. Breen, P.D. Wagner. Effect of Captopril on Skeletal Muscle Angiogenic Growth Factor Responses to Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 88:1690-1697.
- Siafakas NM, Jordan M, Wagner H, Breen EC, Benoit H, Wagner PD. Diaphragmatic Angiogenic Growth Factor mRNA Responses to Increased Ventilation Caused by Hypoxia and Hypercapnia. Eur Respir J. 2001 Apr;17(4):681-7.
- Olfert IM, Breen EC, Mathieu-Costello O, Wagner PD. Chronic Hypoxia Attenuates Resting and Exercise-Induced VEGF, Flt-1, and Flk-1 mRNA Levels in Skeletal Muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2001 Apr;90(4):1532-8.
- Olfert IM, Breen EC, Mathieu-Costello O, Wagner PD. Skeletal Muscle Capillarity and Angiogenic mRNA Levels after Exercise Training in Normoxia and Chronic Hypoxia. J Appl Physiol. 2001 Sep;91(3):1176-84.
- Tang, K., E.C. Breen and P.D. Wagner. Hu Protein R (HuR) Mediated Post-transcriptional Regulation of VEGF Expression in Rat Gastrocnemius Muscle. American Journal of Physiology Heart Circulation. 2002 Oct;283(4):H1497-504.
- Brutsaert TD, Gavin TP, Fu Z, Breen EC, Tang K, Mathieu-Costello O, Wagner PD. Regional differences in expression of VEGF mRNA in rat gastrocnemius following 1 hr exercise or electrical stimulation. BMC Physiol. 2002 Jun 19;2(1):8.
- Breen EC, Tang K. Calcyclin (S100A6) regulates pulmonary fibroblast proliferation, morphology, and cytoskeletal organization in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2003 Mar 1;88(4):848-54.
- Tang K, Breen EC, Gerber HP, Ferrara NM, Wagner PD. Capillary regression in vascular endothelial growth factor deficient skeletal muscle. Physiol Genomics. 2004 Jun 17;18(1):63-9.
- Tang K, Breen EC, Wagner H, Brutsaert TD, Gassmann M, Wagner PD. HIF and VEGF relationships in response to hypoxia and sciatic nerve stimulation in rat gastrocnemius. Respiratroy Physiology & Neurobiology. 2004 Nov 30;140 (1):71-80.
- Tang K, Rossiter HB, Wagner PD, Breen Lung-targeted VEGF inactivation leads to an emphysema phenotype in mice. J Appl Physiol. 2004 Oct;97(4):1559-66; discussion 1549. Epub 2004 Jun 18. Highlighted Topics Series “Lung Growth and Repair”
- Olfert IM, Breen EC, Gavin TP, Wagner PD. Temporal thrombospondin-1 mRNA response in skeletal muscle exposed to acute and chronic exercise. Growth Factors. 2006 Dec;24(4):253-9.
- Scadeng M, Rossiter HB, Dubowitz DJ, Breen High-resolution three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of mouse lung in situ. Invest Radiol. 2007 Jan;42(1):50-7.
- Rossiter HB, Scadeng M, Tang K, Wagner PD, Breen EC. Doxycycline treatment prevents alveolar destruction in VEGF-deficient mouse lung. J Cell Biochem. 2008 May 15;104(2):525-35. PubMed PMID: 18181212.
- Baker ME, Ruggeri B, Sprague LJ, Eckhardt-Ludka C, Lapira J, Wick I, Soverchia L, Ubaldi M, Polzonetti-Magni AM, Vidal-Dorsch D, Bay S, Gully JR, Reyes JA, Kelley KM, Schlenk D, Breen EC, Sásik R, Hardiman G. Analysis of endocrine disruption in Southern California coastal fish using an aquatic multispecies microarray. Environ Health Perspect. 2009 Feb;117(2):223-30. Epub 2008 Aug 28. PubMed PMID: 19270792; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2649224.
- Olfert IM, Howlett RA, Tang K, Dalton ND, Gu Y, Peterson KL, Wagner PD, Breen EC. Muscle-specific VEGF deficiency greatly reduces exercise endurance in mice. J Physiol. 2009 Apr 15;587(Pt 8):1755-67. Epub 2009 Feb 23. PubMed PMID: 19237429; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2683962.
- Tang K, Xia FC, Wagner PD, Breen EC. Exercise-induced VEGF transcriptional activation in brain, lung and skeletal muscle. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2010 Jan 31;170(1):16-22. Epub 2009 Oct 21. PubMed PMID: 19853064; PubMed Central PMCID:PMC2826189.
- Tang K, Wagner PD, Breen EC. TNF-alpha-mediated reduction in PGC-1alpha may impair skeletal muscle function after cigarette smoke exposure. J Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;222(2):320-7. PubMed PMID: 19859910.
- Olfert IM, Howlett RA, Wagner PD, Breen EC. Myocyte vascular endothelial growth factor is required for exercise-induced skeletal muscle angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Oct;299(4):R1059-67. Epub 2010 Aug 4. PubMed PMID: 20686173; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2957383.
- Oakes JM, Scadeng M, Breen EC, Marsden AL, Darquenne C. Rat airway morphometry measured from in situ MRI-based geometric models. J Appl Physiol. 2012 Jun;112(11):1921-31. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00018.2012. Epub 2012 Mar 29. PubMed PMID: 22461437; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3379152.
- Breen EC, Malloy JL, Tang K, Xia F, Fu Z, Hancock RE, Overhage J, Wagner PD, Spragg RG. Impaired pulmonary defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in VEGF gene inactivated mouse lung. J Cell Physiol. 2013 Feb;228(2):371-9. doi:10.1002/jcp.24140. PubMed PMID: 22718316; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3484242.
- Tang K, Murano G, Wagner H, Nogueira L, Wagner PD, Tang A, Dalton ND, Gu Y, Peterson KL, Breen EC. Impaired exercise capacity and skeletal muscle function in a mouse model of pulmonary inflammation. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013 May;114(9):1340-50. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00607.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PubMed PMID: 23449936; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3656431. Highlighted Topic Series “Muscle Dysfunction in COPD”
- Oakes JM, Scadeng M, Breen EC, Prisk GK, Darquenne C. Regional distribution of aerosol deposition in rat lungs using magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013 May;41(5):967-78. doi: 10.1007/s10439-013-0745-2. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PubMed PMID: 23354670; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3625510.
- Delavar H, Nogueira L, Wagner PD, Hogan MC, Metzger D, Breen EC. Skeletal Myofiber VEGF Is Essential for the Exercise Training Response In Adult Mice. American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 12 Feb. 2014 Apr 15:306(8):R586-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00522.2013.
- Oakes J, Breen E, Scadeng M, Tchantchou G, and Darquenne C. Mri-based measurements of aerosol deposition in the lung of healthy and elastase-treated rats. J Appl Physiol. 2014 June 15;116(12): 1561-7. Doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01165.2013.
- Tang K, Gu Y, Dalton ND, Wagner H, Peterson KL, Wagner PD, Breen EC. Selective Life-Long Skeletal Myofiber - Targeted VEGF Gene Ablation Impairs Exercise Capacity in Adult Mice. J Cell Physiol. 2015 Jul 22;PubMed PMID: 26201683.
- Huey KA, Smith SA, Sulaeman A, Breen EC. Skeletal myofiber VEGF is necessary for myogenic and contractile adaptations to functional overload of the plantaris in adult mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016 Jan 15;120(2):188-95. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00638.2015. Epub 2015 Nov 5. PubMed PMID: 26542520; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4719059.
- Knapp AE, Goldberg D, Delavar H, Trisko BM, Tang K, Hogan MC, Wagner PD, Breen EC. Skeletal myofiber VEGF regulates contraction-induced perfusion and exercise capacity but not muscle capillarity in adult mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):R192-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00533.2015. Epub 2016 May 25. PubMed PMID: 27225953; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4967234.
- Breen EC, Scadeng M, Lai NC, Murray F, Bigby TD. Functional magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo quantification of pulmonary hypertension in the Sugen5416/hypoxia mouse. Exp Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;102(3):347-353. doi:10.1113/EP086067. Epub 2017 Feb 14. PubMed PMID: 27897352.
- Alasmari F, Crotty Alexander LE, Nelson JA, Schiefer IT, Breen E, Drummond CA, Sari Y. Effects of chronic inhalation of electronic cigarettes containing nicotine on glial glutamate transporters and α-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptorin female CD-1 mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Mar 27;77:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.03.017. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID:28347687.
- Benjamin Rich1, Miriam Scadeng2, Yamaguchi M.3, Peter D. Wagner1, Ellen C. Breen1. Skeletal myofiber VEGF is required for the exercise training-induced increase in dentate gyrus neuronal precursor cells. 2017. Journal of Physiol. 2017 Sep1;595(17):5931-5943. doi: 10.1113/JP273994. Epub 2017 Jun 28. PubMed PMID: 28597506; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5577548
- Crotty Alexander LE, Drummond CA, Hepokoski M, Mathew DP, Moshensky A, Willeford A, Das S, Singh P, Yong Z, Lee JH, Vega K, Du A, Shin J, Javier C, Tian J, Brown JH, Breen EC. Chronic Inhalation of E-Cigarette Vapor Containing Nicotine Disrupts Airway Barrier Function and Induces Systemic Inflammation and Multi-Organ Fibrosis in Mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Jan 31. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00270.2017. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 29384700.
- Leonardo Nogueira, Breanna M Trisko, Frederico L Lima-Rosa, Jason Jackson, Helena Lund-Palau, Masahiro Yamaguchi, and Ellen C. Breen. Cigarette smoke directly impairs skeletal muscle function through capillary regression and altered myofiber calcium kinetics in C57BL/6J mice.J Physiol. 2018 Jul;596(14):2901-2916. doi: 10.1113/JP275888. Epub 2018 Jun 19. PubMed PMID:29797443; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6046067. Role: Original idea, experimental design, collection of data, preparation of manuscript for publication.
- Okerblom J, Fletes W, Patel HH, Schenk S, Varki A, Breen EC. Human-like Cmah inactivation in mice increases running endurance and decreases muscle fatigability: implications for human evolution. Proc Biol Sci. 2018 Sep 12;285(1886). pii: 20181656. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.1656. PubMed PMID: 30209232; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6158528. Role: Experimental design, collection of data, preparation of manuscript for publication
- Lee JH, Hailey KL, Vitorino SA, Jennings PA, Bigby TD, Breen EC. Cigarette Smoke Triggers IL-33-associated Inflammation in a Model of Late-Stage Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Nov;61(5):567-574 doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0402OC. PubMed PMID: 30973786; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6827064. Role: Original idea, experimental design, collection of data, preparation of manuscript for publication
- Cannon DT, Rodewohl L, Adams V, Breen EC, Bowen TS. Skeletal myofiber VEGF deficiency leads to mitochondrial, structural, and contractile alterations in mouse diaphragm. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Nov 1;127(5):1360-1369. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00779.2018. Epub 2019 Sep 5. PubMed PMID: 31487223; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6879833. Role: Experimental Design, collection of data, preparation of manuscript for publication
- Sulaeman A, Fine J, de Vargas-Machuca A, Wagner PD, Fruttiger M, Breen EC. Synergistic effect of VEGF gene inactivation in endothelial cells and skeletal myofibers on muscle enzyme activity, capillary supply and endurance exercise in mice. Exp Physiol. 2020 Sep 16. doi: 10.1113/EP088924. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 32936962. Role: Original idea, experimental design, collection of data, preparation of manuscript for publication
- Rodriguez M, Chen J, Jain PP, Babicheva A, Xiong M, Li J, Lai N, Zhao T, Hernandez M, Balistrieri A, Parmisano S, Simonson T, Breen E, Valdez-Jasso D, Thistlethwaite PA, Shyy JY, Wang J, Garcia JGN, Makino A, Yuan JX. Upregulation of Calcium Homeostasis Modulators in Contractile-To-Proliferative Phenotypical Transition of Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells. Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 2;12:714785. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.714785. PMID: 34408668; PMCID: PMC8364962.
- Cannon DT, Nogueira L, Gutierrez-Gonzalez AK, Gilmore NK, Bigby TD, Breen EC. Role of IL-33 receptor (ST2) deletion in diaphragm contractile and mitochondrial function in the Sugen5416/hypoxia model of pulmonary hypertension. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2022 Jan;295:103783. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2021.103783. Epub 2021 Sep 8. PMID: 34508866. Role: Contributed to the original idea and experimental design, provided the mouse models, edited the final manuscript
- Indralingam CS, Gutierrez-Gonzalez AK, Johns SC, Tsui T, Cannon DT, Fuster MM, Bigby TD, Jennings PA, Breen EC. IL-33/ST2 receptor-dependent signaling in the development of pulmonary hypertension in Sugen/hypoxia mice. Physiol Rep. 2022 Feb;10(3):e15185. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15185. PMID: 35150208; PMCID: PMC8839421. Role: Concept and experimental design, provided the mouse models, trained the students who performed the experiments, data collection, preparation manuscript for publication
- Nogueira L, Zemljic-Harpf AE, Yusufi R, Ranjbar M, Susanto C, Tang K, Mahata SK, Jennings PA, Breen EC. E-cigarette aerosol impairs male mouse skeletal muscle force development and prevents recovery from injury. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Dec 1;323(6):R849-R860. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00314.2021. Epub 2022 Oct 17. PMID: 36250633; PMCID: PMC9678407. Role: Original idea, experimental, design, collection of data performed lengthening contractions and collected confocal images, preparation of manuscript for publication.
- Wang D, Li X, Duong T, Li W, Wang H, Kleschevnikova N, Patel HH, Breen E, Powell S, Wang S, Head B. Nicotine Inhalant via E-Cigarette Facilitates Sensorimotor Function Recovery by Upregulating Neuronal BDNF-TrkB Signaling in Traumatic Brain Injury. Authorea. 2023 DOI: 10.22541/au.169816532.21605099/v1. Role: Experimental design and collection of data.
Invited Articles, Book Chapters, etc.
- Lian, J.B., G.S. Stein, T.A. Owen, R. Bortell, V. Shalhoub, J. Bidwell, E. Breen, L.M. Barone, A. van Wijnen, and M. Aronow. 1991. Regulation of Osteocalcin Gene Expression During Growth and Differentiation of the Bone Cell Phenotype. In: The Biological Mechanism of Tooth Movement and Craniofacial Adaptation Davidovitch, Z. (ed), EBSCO Media, Birmingham, Alabama, pp. 159-179. (Book Chapter)
- Lian, J.B., G.S. Stein, T.A. Owen, R. Bortell, H. DeLuca, J. Bidwell and E. Breen. Vitamin D Regulation of the Bone Specific Osteocalcin Gene is Functionally Related to Osteoblast Growth and Differentiation. In: Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Vitamin D. Norman, A.W. (ed), Paris, France. pp. 12-20. (Book Chapter)
- Breen, E. and K.R. Cutroneo. Biochemical and Molecular Aspects of Pulmonary Fibroblasts Heterogeneity. In: Pulmonary Fibroblast Heterogeneity, Phipps, R., (ed), CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Florida. pp. 27-54. (Book Chapter)
- Stein, G.S., J.B. Lian, T.A. Owen, J.P. Bidwell, V. Shalhoub, E. Breen, A.J. van Wijnen, and J.L. Stein. Contributions of Cell Structure to Integrated Expression of Cell Growth in Tissue-Specific Genes During Osteoblast Differentiation. In: Chemistry and Biology of Mineralized Tissues. Slavkin, H. and Price P. (eds), Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp. 277-295. (Book Chapter)
- Stein, G.S., J.B. Lian, T. Owen, B. Bortell, A.J. van Wijnen, J.P. Bidwell, E.C. Breen, and S.I. Dworetzky. Integrated Relationship of Proliferation and Differentiation During Osteoblast Phenotype Development. In: Frontiers of Osteosarcoma Research. Novak, J.S. and McMaster, J.H.(eds), Hogrese and Huber, pp. 387-402. (Book Chapter)
- J.B., E.C. Breen and O. Mathieu-Costello. 1998. Strength, Failure, and Remodeling of the Pulmonary Blood-Gas Barrier. In: Pulmonary Edema. Weir, E.K. and Reeves, J.T. (Eds), Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY. (Book Chapter)
- Wagner, P.D. and Breen, E.C. Angiogenesis –Lessons Learned from Skeletal Muscle. In: Bronchial Vascular Remodeling in Asthma and COPD, A. Lazar, Ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc. 2005
- Wagner, P.D., I.M. Olfert, K. Tang and E.C. Breen. Muscle-Targeted Deletion of VEGF and Exercise Capacity in Mice. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology 151(2-3):159-66.
- Breen VEGF in Biological Control. J Cell Biochem. 2007 Dec 15;102(6):1358-67. Review.
- Breen C., Tang K., Olfert, M., Knapp, A., Wagner, P.D. Skeletal muscle capillarity during hypoxia: VEGF and its activation. High Altitude Medicine & Biology. 2008, 9(2):158-66. Review. PubMed PMID: 18578647. (from accepted).
- Rossiter HB, Breen Commentaries on viewpoint: use of mean airspace chord length to assess emphysema. Assessment of emphysema benefits from quantification of heterogeneity. J Appl Physiol. 2008 Dec;105(6):1983-4; author reply 1986-7. PubMed PMID: 19140248.
- Breen EC and Yuan J.X.-J. Gene Cloning Transfections and Mutageneis. In: Textbook of Pulmonary Vascular Disease (Eds.) J.X.-J. Yuan; J..N. Garcia; C.A. Hales; S.Rich; S.L. Archer; J.B. West. 1st, 2011, XXXII, ISBN 978-0-387-87428-9. Springer (Book Chapter)
- Breen E, Yuan JX. Targeting ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels to Treat Pulmonary Hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 May;66(5):476-478. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0549ED. PMID: 35238728; PMCID: PMC9116352. Role: Prepared first draft of manuscript and edited final version.
- Nogueira L, Breen Cigarettes Make You Weak: RANKL/RANK Link Changes in Muscle and Bone. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 May;64(5):533-535. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0098ED. PMID: 33711242; PMCID: PMC8086038. Role: Research, writing and editing of final manuscript.
Conference Proceedings
- Breen, E.C., V.M. Falco, M. Absher, and K.R. Cutroneo. 1989. A Novel Method for Isolating Rat Lung Fibroblast Subsets. Platform Session #3 Cell Differentiation; East Coast Connective Tissue Society, Ninth Annual Meeting.
- Breen, E.C. 1991. Role of Rat Lung Fibroblasts and Subpopulations in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis.
- Stein, G., T. Owen, J. Bidwell, R. Bortell, V. Shalhoub, E. Breen, J. Lian, and G. Stein. 1991. Contribution of Cell Structure to Integrated Expression of Cell Growth and Tissue Specific Genes During Osteoblast Differentiation. 4TH International Conference on Mineralized Tissues.
- Parker, J.C., E.C. Breen and J.B. West. 1996. Mechanical Strain Increases Expression of mRNA for Microvascular Interstitial Matrix Proteins in Rat Lungs. American Heart Association Meeting.
- Wagner, P., J. Roca, T. Gavin, M. Jordan, N. Siafakas, H. Benoit, H. Wagner, E. Breen. 1997. Acute Skeletal Muscle Angiogenic Growth Factor Responses to Exercise are not Mediated by Increased Blood Flow. Biomedicine Meeting.
- West, J.B., J.T. Berg, E.C. Breen, Z. Fu and O. Mathieu-Costello. Effect of High Capillary Pressure on the Blood-Gas Barrier. XXXIII International Congress of Physiological Sciences IUPS
- Healthy Learning DVD. Integrated Respiratory and Cardiovascular Responses to Hypoxia. Featured Science Session. 58th Annual ACSM Meeting, May 31 June 4 2011 Denver CA
- Breen EC, Prisk GK, Darquenne, C. Setting the Stage for Rapid Assessment of Celestia Dust Toxicity. In: The Impact of Lunar Dust on Human Exploration, held 11-13 February, 2020 in Houston, Texas. LPOI Contribution 2141, 2020, id.5017










